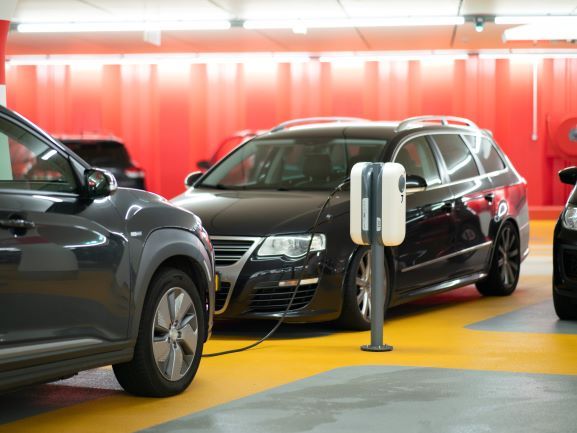
Hey there! I bet at some point, you’ve been amazed by an electric toy car zipping around all on its own. Powered by a battery, it delivers hours of fun—until it doesn’t. When the battery dies, the fun grinds to a halt, and you’re left scrambling for a charger or replacement.
Sound familiar? That experience isn’t just for kids anymore. Adults now face a similar situation, only on a much larger scale. The cars of the future are already on our roads—and yes, they too rely on batteries. Welcome to the fast-evolving world of electric vehicles (EVs).
From Petrol Pumps to Power Plugs: The Rise of the Electric Vehicle
Today, most vehicles you see still rely on petrol, diesel, or compressed natural gas. But a quiet revolution is underway. Electric vehicles—powered wholly or partially by electricity—are becoming more common on roads around the world.
This shift is driven by several urgent global concerns: climate change, rising urban pollution, and the long-term costs of fossil fuel dependence. EVs are emerging as a practical and powerful solution to these challenges.
Here’s why they matter:
- Zero tailpipe emissions: EVs don’t release exhaust gases while driving, reducing pollution and improving air quality.
- Smooth, quiet rides: With fewer moving parts and no engine noise, electric vehicles offer a refined, peaceful driving experience.
- Lower running costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than petrol, and EVs require less maintenance over time due to fewer mechanical components.
Electric cars are fast becoming more than just a trend—they’re a key part of the future of transportation. But that doesn’t mean the road to full adoption is without its bumps.
The Big Hurdles: Why Isn’t Everyone Driving an EV Yet?
Despite all their benefits, electric vehicles still face significant challenges. These are the main reasons many people are holding back from making the switch:
EVs often cost more upfront than their petrol or diesel counterparts. The primary reason is the high cost of the battery. However, as production scales up and battery technology improves, prices are steadily declining. Some countries also offer government incentives to help make EVs more affordable.
Range anxiety remains one of the biggest concerns for potential EV buyers. Although many modern EVs can travel between 250 and 500 kilometers on a single charge, drivers are often unsure if that’s enough—especially for long trips or in areas with limited charging infrastructure.
Unlike refueling a traditional car, charging an EV isn’t instant. Home charging can take between 6 to 12 hours depending on the power source. Public fast chargers are much quicker—some can provide an 80 percent charge in under an hour—but they are not yet as widespread as fuel stations.
That’s why battery innovation is at the heart of EV development. To reach mass adoption, we need batteries that last longer, charge faster, and store more energy in smaller, safer packages.
It’s All About the Battery: The Heart of an Electric Car
At the core of every electric vehicle is a large, powerful battery pack. Currently, most EVs use lithium-ion batteries—the same technology found in smartphones, laptops, and other portable electronics.
Lithium-ion batteries are popular for good reason. They are lightweight, rechargeable, and have a high energy density, meaning they store a lot of power for their size. But they aren’t perfect. These batteries can degrade over time, are sensitive to high temperatures, and contain flammable liquid electrolytes that pose safety risks if damaged.
This is where the next generation of batteries comes in—solid-state batteries—a technology that could transform the EV landscape.
To understand what makes solid-state batteries special, it helps to know how a battery works. Each battery has three main parts:
- Anode (negative terminal)
- Cathode (positive terminal)
- Electrolyte, the substance that allows lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode
Traditional lithium-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte and a graphite anode. Solid-state batteries replace the liquid with a solid material, which is more stable and less prone to overheating or leaking.
One of the most promising advances in this space comes from QuantumScape, a California-based startup working on a new kind of solid-state battery. Their innovation lies in removing the traditional anode entirely. Instead, when the battery charges, lithium metal forms naturally on a layer of solid ceramic electrolyte. This simplifies the structure, reduces weight, and increases energy storage.
The result? A battery that is safer, more compact, and much faster to charge. According to QuantumScape, their battery could allow electric vehicles to reach 80 percent charge in just 15 minutes—a massive leap forward compared to today’s charging times.
The Road Ahead: Challenges Beyond the Battery
Even with exciting developments like anode-less solid-state batteries, there are still major hurdles to overcome before this technology becomes mainstream.
Producing solid-state batteries at scale is complex and currently very expensive. Companies are working to streamline production processes, but mass adoption may still be several years away.
Fast-charging networks need to grow rapidly to support a larger number of EVs. Urban areas are starting to see more chargers, but rural and remote regions still lack sufficient coverage. Home charging solutions also need to become more accessible and standardized.
With more EVs on the road, battery disposal and recycling become critical issues. Many of the rare metals used in batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, need to be recovered and reused to ensure long-term sustainability.
Governments, automakers, and tech companies are all investing heavily in solving these problems. The transition won’t happen overnight, but the momentum is clearly building.
So, Are We There Yet?
Not quite. But we’re getting closer every day.
Electric vehicles are moving from novelty to necessity, and the battery breakthroughs happening right now will shape how quickly we get there. Companies like QuantumScape, along with major automakers and research institutions, are laying the foundation for an electric future—one where charging is fast, ranges are long, and costs are low.
If the 20th century belonged to oil, the 21st may very well belong to electrons. As technology continues to evolve, the next car you drive—or even the next one you dream about—might just be powered by one of these super-batteries.
So the next time you see an EV glide silently past you, remember: under that hood is not just a motor. It’s the future of mobility.
Learn More:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid-state_battery
- https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/feb/04/solid-state-batteries-inside-the-race-to-transform-the-science-of-electric-vehicles
- https://time.com/6358257/lithium-ion-solid-state-ev-battery-innovation
- https://www.marketwatch.com/story/nissan-wants-to-take-the-lead-in-next-generation-solid-state-ev-batteries-ae5d715a
- https://www.ev-global.org/blogs/articles/Article12_SolidState_Batteries
Footnote: The development of electric vehicles is a prime example of cutting-edge STEM innovation. The research studies behind advanced batteries combine environmental science (addressing climate change) with the science of advanced materials and analytical chemistry to create safer, more efficient power sources. The research methodology in this field is highly advanced, driving a wave of new technology. As a result, breakthroughs are constantly published in top international journals and scholarly sources, making it a vital subject for any scholar in engineering or material science.